Frankincense
(Boswellia sacra)
Luban in Arabic (tree milk), Olibanum in latin, Libanose/Libanotos in Greek, Lebona in Hebrew, and neter-sent in ancient Egypt.
Frankincense is from old French word and means pure incense. Frankincense is the tree sap.
The genera Boswellia and Commiphora both belong to the family Burseraceae which is characterized by heavy resin ducts in their bark from which the resins frankincense and myrrh are obtained.
Boswellia is named after John Boswell, the Scottish botanist.
Boswellia sacra specie is genetically the origin of other species, the closest is Boswellia carteri.
Boswellia sacra is native to southern Arabia, Boswellia carteri and frereana are native to African horn while Boswellia serrata is native to India.
A European Renaissance Visualization of frankincense harvest in Oman
Frankincense trees grow in a fairly restricted habitat. They prefer the arid zone behind the monsoon mountains, beyond the reach of the monsoon rain, but within the reach of the cool winds which blow steadily during this season.
Frankincense trees are mostly to be found growing on the lower slopes and down in the base of gullies and run-offs, or more thickly along the broader floors of the larger wadis, rarely being able to survive on the higher ridges or the high raised plateaux.
Boswellia sacra sap
Medicinally, frankincense resin was used in the treatment of almost every imaginable disease by Greek and Roman physicians and remedies employing frankincense also appear in the Syriac Book of Medicine, in the texts of the Muslims practitioners of the Middle Ages, and in Indian and Chinese medical writings.
Scientifically, it’s more accurate to call frankincense sap as oleo-gum-resin as it consists of essential oil, polysaccharides gum, and terpenoid resin.
The biblical 3 Magi
Three kings (also known as the three wise men) had a mission to go to Bethlehem. They followed a star that showed them the way to see baby Jesus, who had just been born. Upon arriving, these three kings offered three gifts: Frankincense, myrrh, and gold.
THE THREE MAGI - A BYZANTINE MOSAIC
Frankincense, myrrh and gold (that we believe its Commiphora gileadensis oil) were the three magi gifts to baby Jesus.
Frankincense is mentioned 22 times in the Bible; 16 times for religious worship, twice as a tribute of honor, once as an article of merchandise, and 3 times as a product of the royal garden of Solomon. Frankincense is included in the formulation of the holly incense handed down by God to Moses.
Today, an acceptable incense in Roman Catholic churches is composed of 1/15 storax, 4/15 benzoin, and 10/15 frankincense.
Boswellia sacra grows only in southern Arabia in Oman and Yemen, and is the only Boswellia specie in Oman.
Boswellia sacra
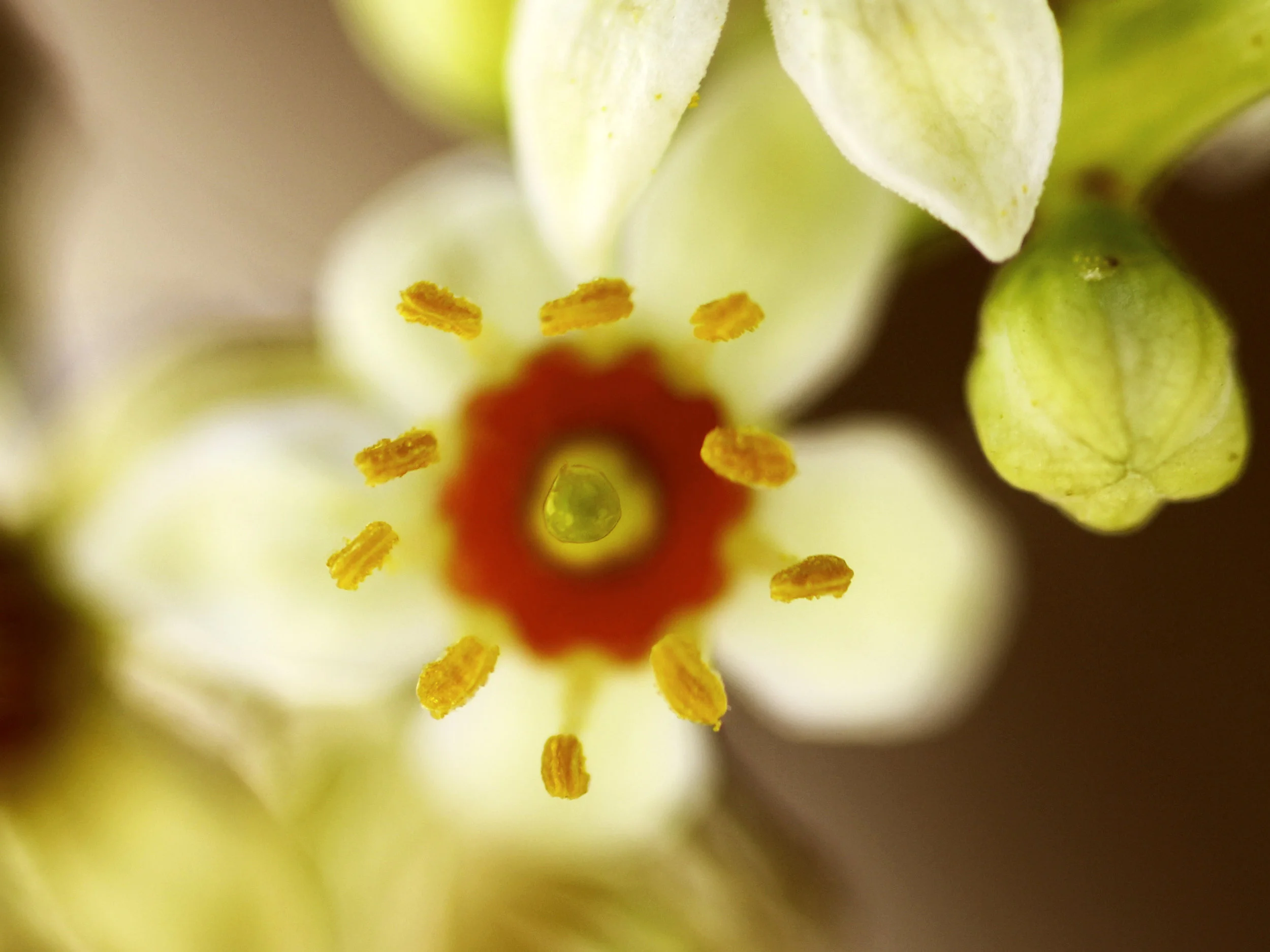
A tip of shoot showing pinnately dissected leaves and racemes of flowers and fruits; B raceme showing gradual development of buds to opened flowers to fruits; C flower showing corolla, stamens, disc, and gynoecium; D stamen; E as the flower ages the anthers drop from the filaments and the disc turns from yellow to red; F as the young fruit develops the petals fall and the disc further darkens; G fruit; H dehiscing fruit.
Plants of Dhofar: The Southern Region ofOman :Traditional, Economic and Medicinal Uses
Authors Anthony G. Miller, Miranda Morris, Susanna Stuart-Smith
Illustrated by Susanna Stuart-Smith.
Boswellia sacra tree grow to an average of 5 meters tall, and may reach to 10-12 meters, with a single trunk or more commonly, several from base, with papery peeling bark.
Winter is the flowering period and may extend to April. Nectariferous ring of flowers change colors with significant ecological role through 3 phases; Yellow, Orange-Red, and dark red phases.
Yellow flowers are visited by a large number of different pollinators starting from half an hour after sunrise until the sunset; bees, wasps, ants, little flies and butterflies. Red flowers are not visited. orange flowers are visited mostly by walking insects.
Fruits usually begin to ripe in March.
Though frankincense trees seem to be favoured by a hot and humid climate and need good access to water to grow well, they will survive under considerably drier conditions. Always prefer dolomitic limestone or limestone only. Boswellia sacra us easy to propagate from cuttings and given the right conditions the will grow well. Germination rate is low and even more lower if the tree is over-harvested for frankincense. Adult Boswellia mortality is 6-7% per year independent from sap tapping.
Samhan Nature Reserve park; 17° 8′ 7.8″ N, 54° 47′ 29.76″ E, is one of the largest natural reservations in southern Oman of 4,500 km² area. It’s the native land of Hougari grade frankincense, the most common grade of Boswellia sacra. Boswellia sacra trees grow in 50% of its area with density of 2.3 tree/hectare (1km²=100hectare) and an average annual frankincense yield of 3.3kg/tree, in its southern wadis.
It’s estimated that Boswellia sacra native area is about 4000 km² in Dhofar.
Harvesting frankincense sap from Boswellia sacra.
Al manqaf is a unique iron knife which the Dhofari people use to cut then harvest frankincense sap.
Cross section in Boswellia sacra mature bark
A special tool called a “mengaff” is used to collect frankincense; One end has a sharp edge used for the decortication and the other end being blunt is used in assisting to remove the exudate when it has hardened. In tapping, a wound of 4-8 cm long, 3 cm wide, and 2.5-4 mm depth (ie not through to the wood) is made in one or more places. After about a fortnight, the exudate which collects as globular pear shaped or club shaped tears is removed and the wound freshened. Further collection is carried out every few weeks. At each collection it is customary to remove only the exudate that collects on the wound itself, that which runs down the stem being left to accumulate and collected annually.
The practice is to suspend tapping of each tree every 5th-6th year to allow resting period, otherwise the trees become exhausted. Under favourable conditions tapping can be started after 5-7 years. The size of the tree will then be 4-5 m and around 15 cm diameter at around 1.3 cm above ground level. Average yield is 2-4 kg/tree per year.
Boswellia sacra Oleo-gum-resin grades:
Najdi Harvested in the desert (dry and hot with low humidity) and characterized by white opacity
Hougari Regular Harvested in mountains and valleys where Monsoon rain is sparse and humidity is average
Hougari GreenThe greenish tinged frankincense resin whichis a variant of the Hougari regular grade.
Sha'bi Dark brownish sap from rainy areas and mostly near coastal areas where humidity is high.
Factors affecting type/grade of frankincense resin:
Pre-Harvest
The climate of trees population
Age of tree
Season of harvest
Technique of cut
Post-harvest
Processing
Time
Freshly harvested frankincense resin is kept rarefied on a plane surface to dry under air so don't stick to each other when handled later. During this traditional post-harvest drying process, some water and monoterpenes of frankincense resin evaporate.
Other common species of Boswellia;B. carteri , B.frereana,and B. serrata. Non of them grow in Oman and B. carteri is the closest species (descendant) to B. sacra.
Frankincense oleo-gum resin consist of 9-11% essential oil (monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes and diterpenes), 27-35% gum (polysaccharides: galactose:arabinose and galactose:galacturonic acid), and 44-59% resin (terpenoids and boswellic acids), 5.5-11% water, and 0-1% ash.
Polysaccharide make the frankincense more cloudy.
Frankincense partially dissolve in water forming immiscible suspension (mucilage).
Wide decortication versus sharp stab frankincense sap.
Frankincense sap of sacra has an incense camphoraceous woody aroma with sweet citrus fragrance note.
Scent, or fragrance, is processed one way through our noses. Aroma is sensed through our nose as well as nasopharynx. Nasopharynx or retronasal is when a smell is first processed via our taste buds.
Boswellia sacra frankincense smell
Boswellia sacra tree typical environment in southern Arabian coast
Frankincense (Boswellia sacra) trees reservation to the west of Salalah - Dhofar
Frankincense (Boswellia sacra) tree farm reservation of about one square kilometer, 7 km to the west of Salalah port, one of two major Boswellia sacra trees reservations in Dhofar state - Sultanate of Oman in addition to the Natural Park of Frankincense Tree in Wadi Dawkah that is about 5 square kilometers.
Satellite image of Dhofar mountains
Dhofar Mountains early morning
Tree thermal zones:
BLUE 18-32 C
YELLOW-GREEN 20-36 C
RED 24-44 C
Traditional Arabic Frankincense Incense Burner
Frankincense Health Benefits
Osteoarthritis
Boswellia anti-inflammatory effects (namely; terpenes and boswellic acids) help reduce symptoms of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis by inhibition of leukotrienes inflammatory mediators at doses of 200-350 mg, three times a day. It increases joint mobility, reduce morning stiffness, increase range of movement, and reduce swelling and pain.
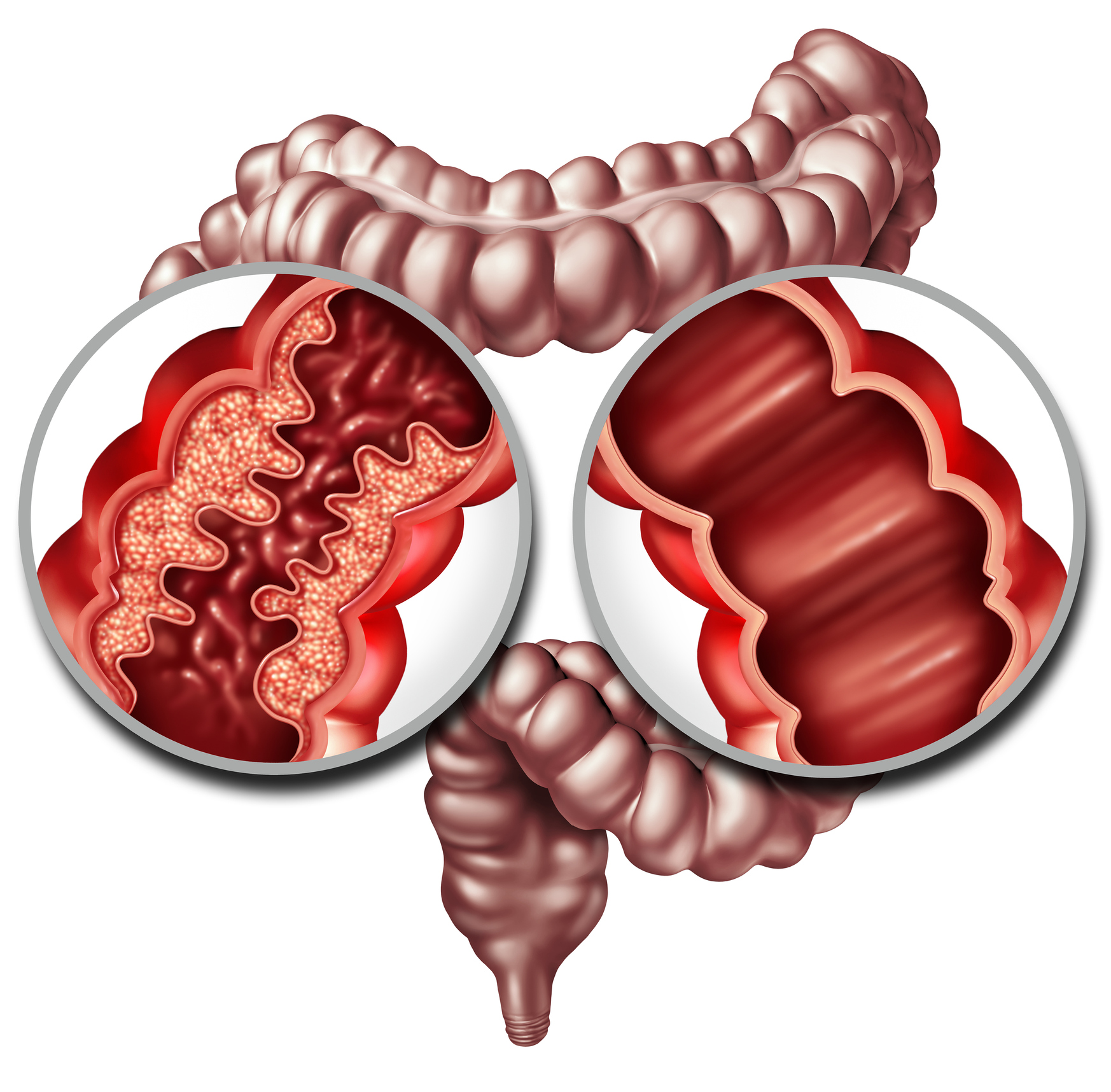
Crohn's disease (Lt) versus normal (Rt)
Frankincense help controlling inflammatory bowel diseases Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis at doses of 1,200 mg, three times a day in Crohn’s disease, and 350–400 mg, three times a day in Ulcerative colitis (both for 6 weeks to show improvement).
Respiratory airways
Frankincense reduce the likelihood of asthma attacks in susceptible people (prophylactic), and relieve asthma symptoms like shortness of breath and wheezing through its leukotrienes inflammatory mediators inhibition. 2/3rd of patients showed improvement of symptoms on doses of 300 mg three times a day for 6 weeks. 3 mg per kg body weight improved lung capacity and helped reduce asthma attacks in people with chronic asthma.
Recommended dose of frankincense extract in asthma is 300–400 mg, three times a day.
cancerous cell
Frankincense compounds help kill cancer cells and prevent tumors metastasis. Boswellic acids of frankincense extract and sesquiterpenes group of its essential oil have anti malignant activities.
Frankincense has shown effect in breast, prostate, pancreatic, skin, and colon cancer cell lines.
4.2 grams of frankincense a day reduced peritumoral oedema in 60% of the patients with brain tumor (glioma).
Early phase of gingivitis and dental carries
Frankincense has a strong antibacterial properties and help prevent bad breath, toothaches, cavities and treat oral infections like mouth sores.
Frankincense extract is effective against aggressive gum infections of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans.
Chewing 200 mg frankincense for 2 weeks can treat gingivitis.
Boswellia frereana is the best boswellia species for chewing purposes.
Normal bladder transitional epithelium
Large doses of frankincense have been used to enhance memory function.
Frankincense oil showed rejuvenating properties on skin and bladder tissue culture.
Note: Frankincense may interact with anti-inflammatory drugs, blood thinners and cholesterol lowering pills.
Frankincense Hydrosol
Hydrosols, distillate waters or floral waters is the aromatic water produced (and as a role; in more quantity than essential oils) during essential oils distillation.
It’s composed of distilled water and the light molecular weight portion of the essential oil that is being distilled.
Sol, in physical chemistry, a colloid (aggregate of very fine particles dispersed in a continuous medium) in which the particles are solid and the dispersion medium is fluid. If the dispersion medium is water, the colloid may be called a hydrosol; and if air, an aerosol.
Generally, hydrosols contain less than 1% of dissolved essential oils and having hydrophilic properties (water-soluble components).
Hydrosols also contain carboxylic acids, hence why their anti-inflammatory activity and its pH of lower than 7.
Tyndall Effect to differentiate solution from colloid that is light scattering by particles in a colloid or in a very fine suspension when applying beam light. Left: solution, and Right: colloid.
Typically, frankincense hydrosol is composed of distilled water plus 1-3% of the lightest molecular weight portion of frankincense essential oil that get dispersed homogeneously into the distilled water during the process of distillation.
Many factors affect frankincense hydrosol “saturation” with the its volatile oil portion including frankincense grade, distillation time, heat flow rate, resin:water ratio, condenser design and efficiency, ambient temperature and others.
Frankincense hydrosol is a transparent to cloudy solution - colloidal solution with yellow tint and a strong frankincense aroma.
Mild Hydrosol: Transparent solution that is physically stable over time.
Saturated Hydrosol: Cloudy colloidal solution that is stable physically over time.
Cohabitation: Cloudy suspension that eventually separate over time into floating essential oil layer over hydrosol.
Frankincense hydrosol is a wonderful skin tonic, has mild analgesic, antimicrobial, anti-ulcer, gastro-protective, and dyspepsia relieving properties plus a memory boasting effect. All mainly attributed to its major component; alpha pinene. Its cholinesterase inhibition enhance memory.
Alpha-pinene is a food additive permitted for direct addition to food for human consumption.
Alpha pinene is typically 78% of Boswellia sacra essential oil but what gives Boswellia sacra hydrosol alpha pinene a higher grade is its colloidal stability into water which means ready bioavailability and easier tissue distribution.
Frankincense (as well as other plant source) alpha pinene has a dissolving effect to kidney stones.
The treatment with terpenes may lead to accelerated stone expulsion. As a combination of naturally available terpenes seems to have the potential to promote and accelerate stone expulsion in primary management of urolithiasis.